

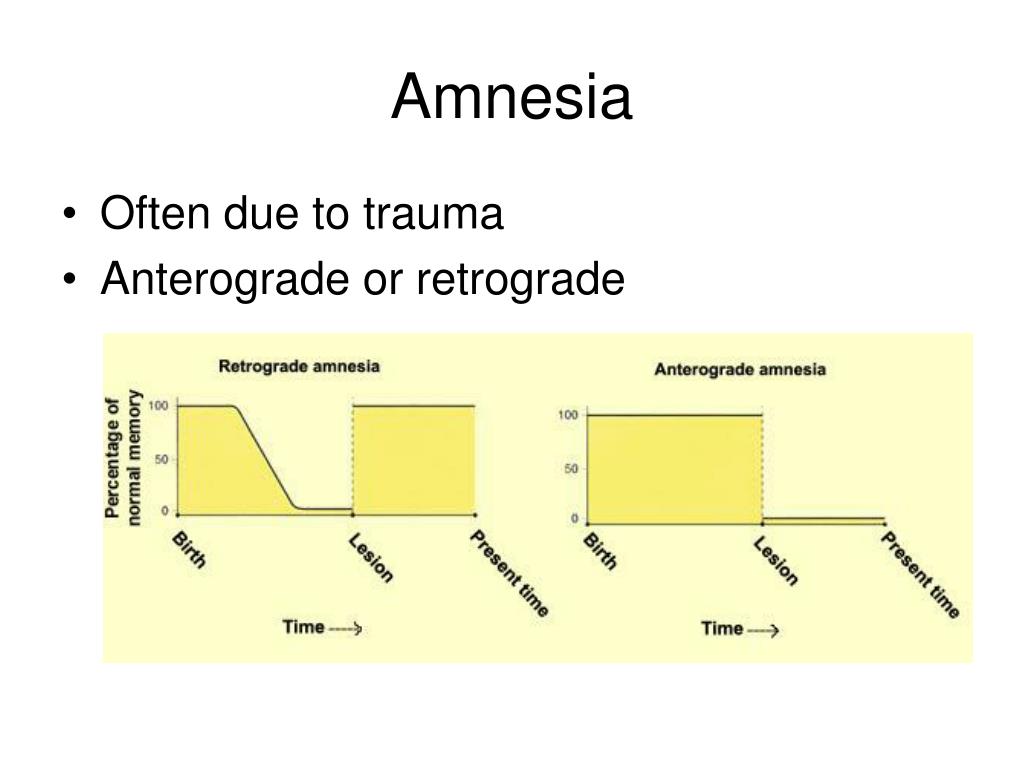
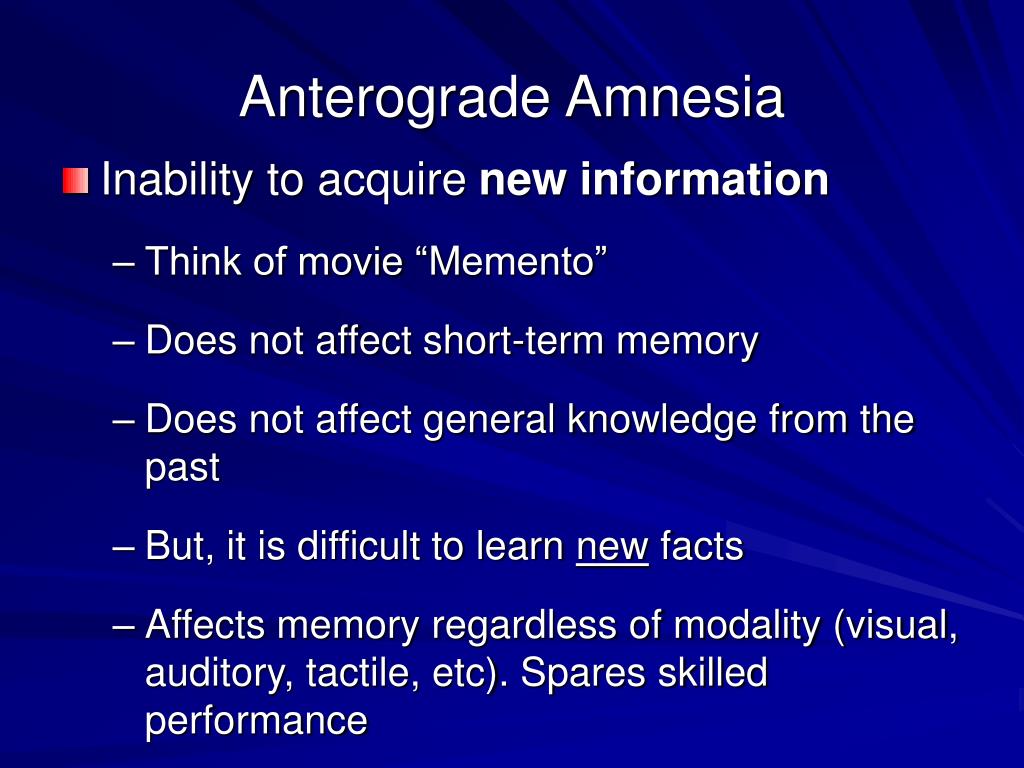
DSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria for Dissociative Amnesia ĭissociative Amnesia has been previously known as Psychogenic Amnesia, and Hysterical Amnesia. The person may struggle to work out what was discussed while trying to avoid the other person realizing this. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation gives the example of forgetting the contents of a conversation from one moment to the next. :298-299 Micro-amnesias are also typical in dissociative disorders, the amnesia is for very, very brief periods of time. Continuous amnesia is unable to form new memories. Systematized amnesia is amnesia for a category of information (e.g., no memory of family, no memory of a specific person, or childhood sexual abuse). Other forms of dissociative amnesia can also occur people with generalized amnesia (the most severe type) may also lose semantic knowledge (previous knowledge about the world) and procedural knowledge (forgetting well-learned skills). Generalized amnesia may involve the complete loss of a person's identity, in addition to all memories of their past. The three common types of dissociative amnesia are localized amnesia, selective amnesia (which may occur along with localized amnesia), and generalized amnesia. Both of these are capable of diagnosing any dissociative disorder and a number of other disorders as well. :298-299 Clinical interviews to diagnose Dissociative Amnesia include the SCID-D (revised) by Dr Marlene Steinberg, and the Dissociative Disorders Interview Schedule (DDIS). :300-301ĭissociative amnesia is more likely in people with a history of multiple adverse childhood experiences (especially if they include physical or sexual abuse), people who have experienced interpersonal violence (for example, domestic violence or physical assaults), and the risk increases with the "severity, frequency, and violence of the trauma". :298-299, Neurocognitive disorders involving memory loss usually include cognitive (thinking) and intellectual impairments in memory, these are not present in people Dissociative Amnesia. ordinarily would be readily remembered (Criteria A)."īecause there is no neurobiological damage or toxicity, and the difficulties are in retrieving a memory which was successfully stored, the amnesia is always "potentially reversible".

Borderline Personality Disorder and Others.Trauma Related Disorders Related Disorders.Overview of Trauma and Stressor-related Disorders.Trauma & Stressor Disorders Trauma & Stressor Disorders.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
